Abstract
Background: Haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) provides an alternative option for patients without HLA-matched donors. Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), engraftment failure, and infectious complications are main causes of non-relapse mortality (NRM). We hypothesized that selective depletion of TCRαβ+ and CD45RA+ naïve T cells will permit hematopoietic engraftment while effectively reducing GVHD and providing donor immune reconstitution through adoptive transfer of donor's mature NK cells, γδ T cells and CD45RO+ memory T cells.
Methods: Mobilized PBSC products were divided into two fractions in 9:1 ratio and depleted using CliniMACS device after labelling with TCRαβ and CD45RA reagents (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergish-Gladbach, Germany) respectively. All except 6 patients received the standard conditioning regimen of fludarabine 160mg/m 2 divided daily over 4 days, thiotepa 10mg/kg divided twice daily for 1 day, and melphalan 70 - 140mg/m 2 for 1 day, in combination with either total lymphoid irradiation 6Gy (n=53) or 7.5Gy (n=12) over 3 equal fractions, or total body irradiation of 2Gy (n=17), or thymoglobulin (n=2). Short term GVHD prophylaxis was given for 30 days to 1 patient using MMF, 73 using tacrolimus, and 2 using sirolimus.
Results: Between January 2017 and July 2021, we transplanted 85 patients, including 78 adults (median age, 48 years; range 20 - 70) and 7 children (median age, 13 years, range 7 - 17), with high risk AML (n=44), ALL (n=19), MDS (n=9), plasma cell neoplasm (n=4), mast cell leukemia (n=1), acute undifferentiated leukemia (n=1), CMMoL (n=2), CML (n=1) and lymphoma (n=2). Patients were infused with TCRαβ and CD45RA depleted grafts containing median of 6.19 x 10 6 (range 3.54 - 20.78) CD34+ cells/kg, 0.00 x 10 4 (range 0 - 0.97) CD45RA+CD3+ cells/kg, and 1.10 x 10 6 (range 0.15 - 11.67) CD45RO+CD3+ cells/kg. TCRαβ depleted graft fraction contained a median of 0.42 x 10 4 (range 0 - 11.30) TCRαβ+ cells/kg, and 7.61 x 10 6 (range 0.62 - 31.84) TCRγδ+ cells/kg. Only 1 patient experienced primary graft failure with no secondary graft failures. All others had engraftment of ANC > 500 cells/µL at median of 12 days (range 8 - 22) and PLT > 20,000 cells/µL at median of 11 days (range 7 - 17). 6 patients with high donor-specific HLA antibodies (DSA) titres engrafted successfully after desensitisation with plasma exchange, rituximab, and immunoglobulin.
29 patients (34%) developed acute GVHD of grade II - IV (Gd II, n=20; Gd III, n=5; Gd IV, n=4), with a cumulative incidence (CI) of grade II-IV and grade III-IV of 31% (95% CI 21-42%) and 11% (95% CI 5-19%) respectively, at 100 days. Chronic GVHD was seen in only 4 patients at a 2-year CI of 6% (95% CI 2-13%).
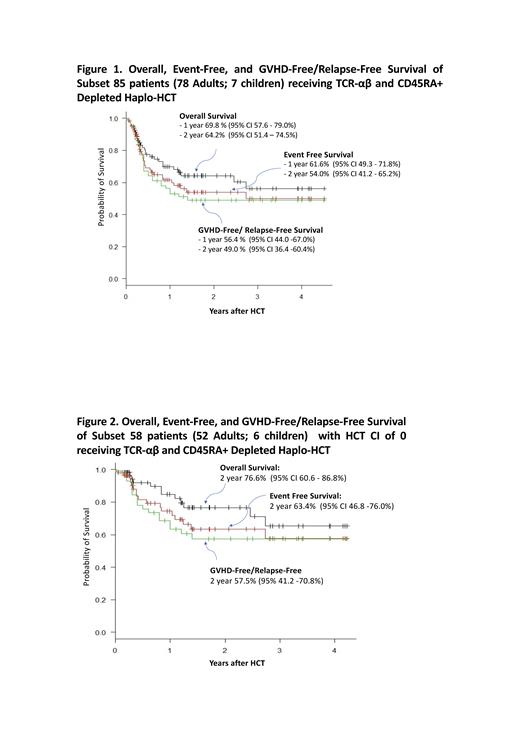
1-year CI of non-relapse mortality (NRM) and relapse were 22.7% (95% CI 13.9 - 32.9%) and 15.7% (95% CI 8.3 - 25.3%) respectively. 4 of the 17 NRM were attributed to aGVHD. Viral reactivation included CMV (n=32), HHV-6 (n=22), EBV (n=15), and adenovirus (n=8). 15 patients (17.6%) died of infection within 180 days, including 6 patients with fatal bacteraemia (bacteria, n=4; candidemia, n=2) and 1 patient from disseminated adenovirus infection. At a median follow up of 448 days (range 16- 1648) in surviving patients, 2-year overall (OS), event-free (EFS), and GVHD-free/relapse-free (GRFS) survival were 64.2 %, 54.0 %, and 49.0%, respectively (Figure 1).
In multivariate analysis, only HCT-comorbidity index (HCT-CI) showed significant impact on OS (HR 3.38; 95% CI 1.42 - 8.02; p=0.0059), EFS (HR 2.62; 95% CI 1.18 - 5.76; p=0.0017), and NRM (HR 4.92; 95% CI 1.79 - 13.58; p=0.0021). Disease risk index (DRI) showed a trend in higher risk of relapse (HR 2.83; 95% CI 0.96 - 8.33; p=0.059). 2-year OS, EFS, and GRFS for the subset of 58 patients (adults, n=52; children, n=6) with HCT-CI score of 0 were 76.6 %, 63.4%, and 57.5 %, respectively (Figure 2).
Conclusions: Our preliminary results suggest that RIC haplo-HCT with TCRαβ and CD45RA+ depleted grafts allow successful allograft in high-risk patients lacking suitable matched donors, including patients with high levels of DSA. Acute GVHD was generally abortive, leading to low incidence of chronic GVHD. Best outcomes are seen in patients with favourable HCT-CI. Further efforts are needed to reduce the risk of infection-related death in patients with high risk HCT-CI, and relapse in patients with high risk DRI, through optimization of anti-microbial prophylaxis or prophylactic infusion of memory-cell DLI.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal